Introduction
When we think of animals, various fascinating creatures come to mind. Land animals, in particular, exhibit a diverse range of characteristics and adaptations. In this article, we will explore fifteen different types of land animals, from mammals and birds to reptiles, insects, and more. Let’s delve into the captivating world of land-dwelling creatures and discover the unique features that define them.
1. Mammals

Mammals form a remarkable group of land animals known for their ability to nurse their young with milk. They encompass a wide range of species, each adapted to thrive in different environments.
1.1 Carnivores
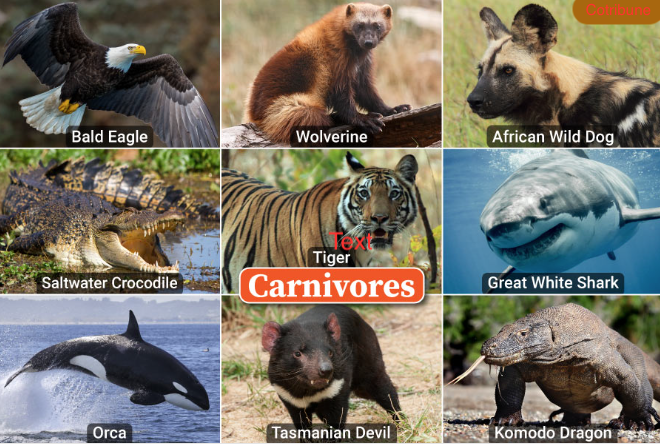

Carnivores are a subgroup of mammals that primarily consume meat. They include iconic predators such as lions, tigers, and wolves. These creatures possess sharp teeth and strong jaws, enabling them to capture and devour their prey effectively.
1.2 Herbivores
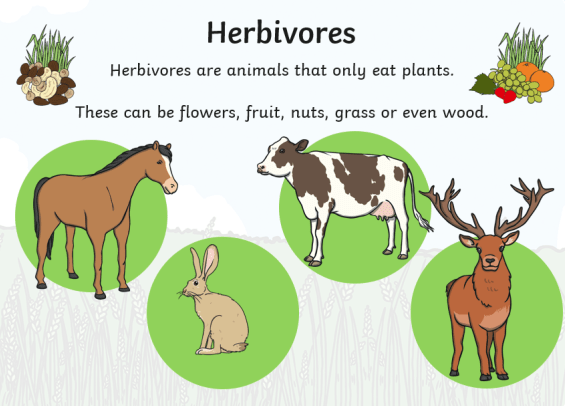
On the other hand, herbivores are mammals that primarily feed on plant matter. Examples of herbivorous land animals include elephants, giraffes, and deer. Their specialized teeth and digestive systems have evolved to process and extract nutrients from plant material.
2. Birds

Birds are another fascinating group of land animals. With their ability to fly, they occupy diverse habitats across the globe. They are characterized by feathers, beaks, and the ability to lay hard-shelled eggs.
3. Reptiles
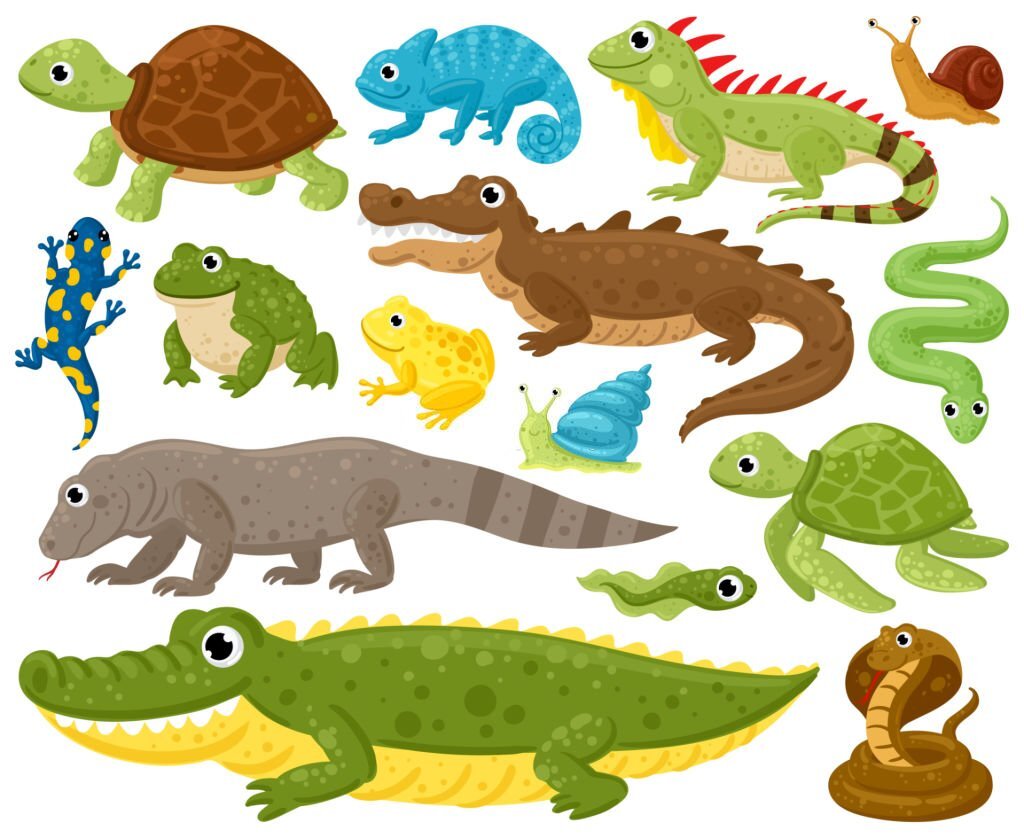

Reptiles, which include snakes, lizards, and turtles, are land animals that have scaly skin and lay soft-shelled eggs. They are known for their cold-blooded nature and various adaptations to different climates.
4. Amphibians
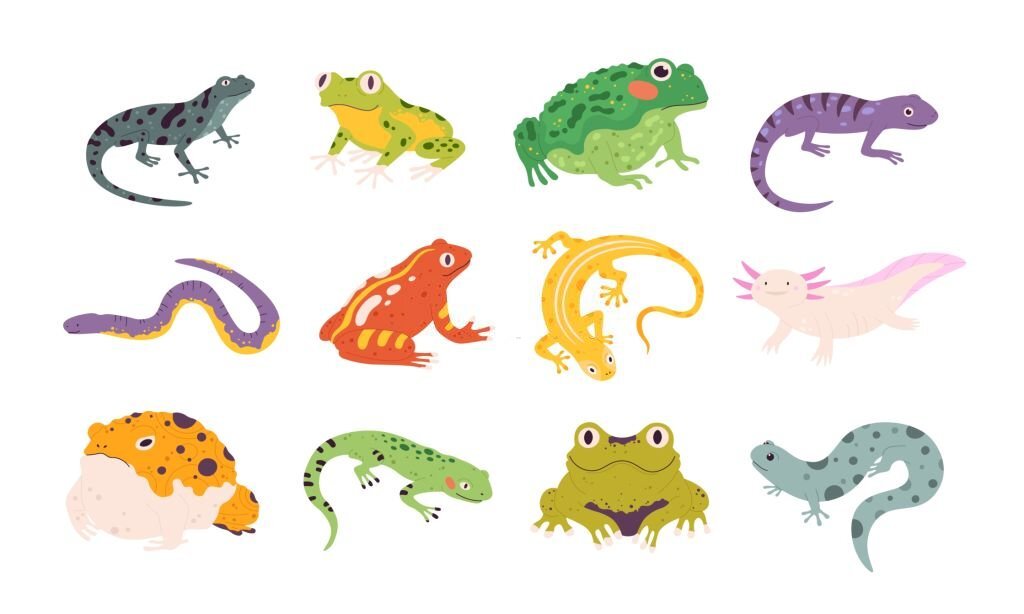

Amphibians, such as frogs, toads, and salamanders, are unique creatures that inhabit both land and water environments. They undergo metamorphosis from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults and rely on their moist skin for respiration.
5. Insects
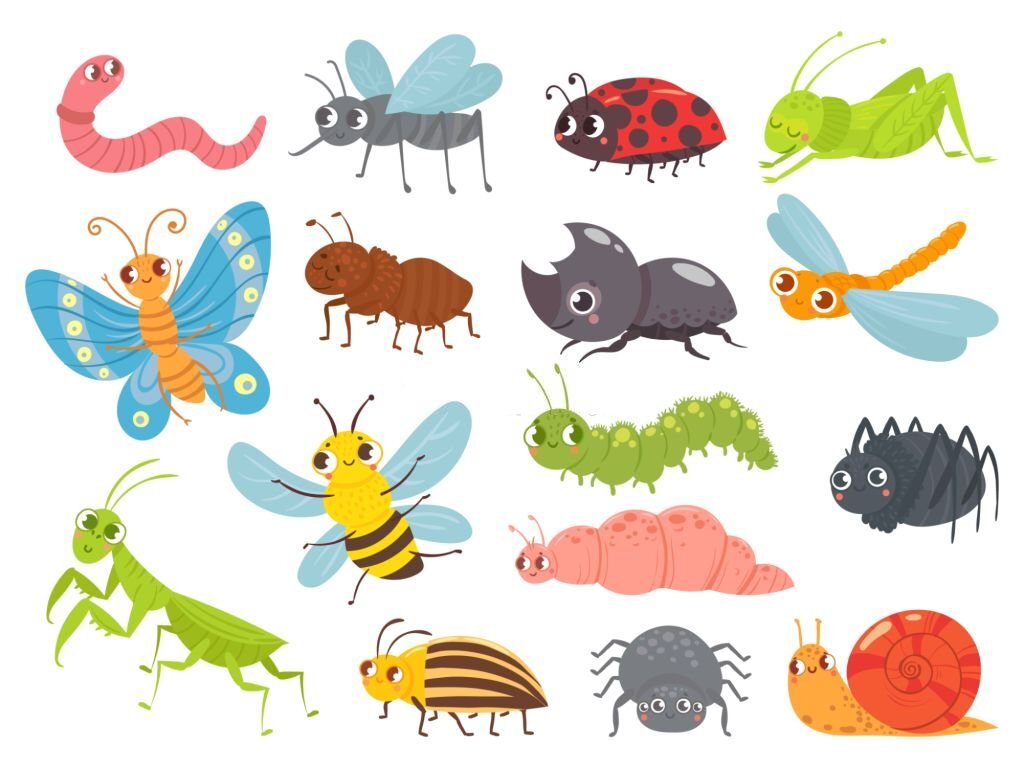

Insects are a diverse group of land animals that dominate terrestrial ecosystems. With their six legs, segmented bodies, and often wings, they exhibit incredible adaptability and play crucial roles in pollination, decomposition, and pest control.
6. Arachnids
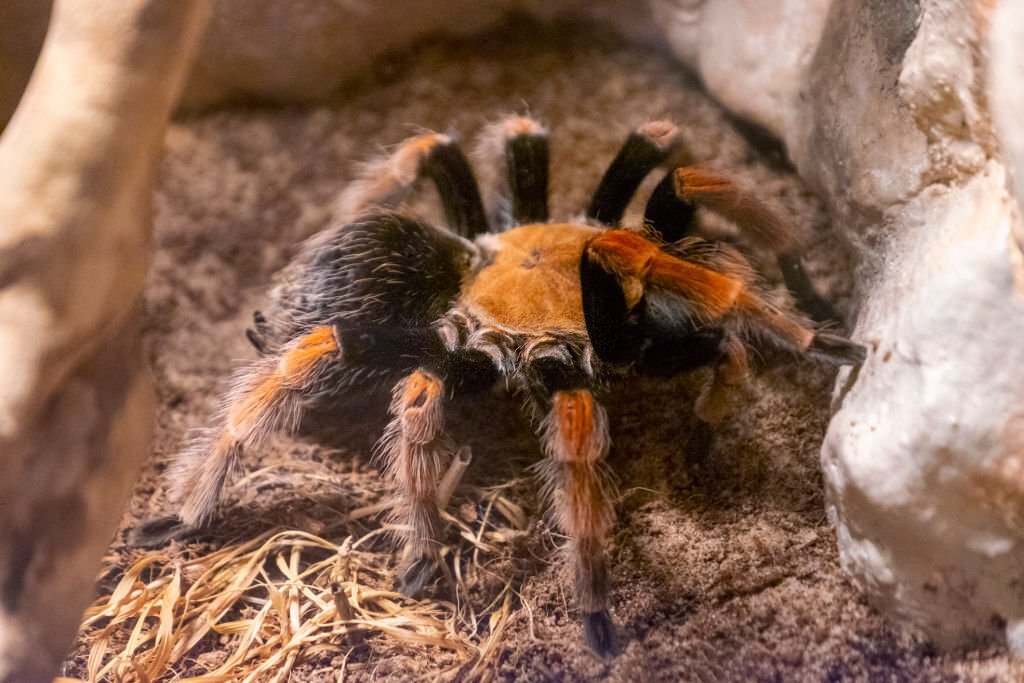

Arachnids, which include spiders, scorpions, and ticks, are land-dwelling creatures characterized by their eight legs and two main body segments. They are essential for regulating insect populations and have unique venomous adaptations.
7. Fish

While fish are primarily associated with aquatic environments, some species have evolved to thrive on land. Land-dwelling fish, such as mudskippers, possess anatomical adaptations that allow them to move and breathe outside of water for extended periods.
8. Crustaceans

Crustaceans, which typically reside in aquatic habitats, also have representatives that venture onto land. Land-dwelling crustaceans, such as terrestrial crabs and pill bugs, have adapted to terrestrial life while still retaining some aquatic features.
9. Mollusks

Mollusks are a diverse group of land animals that include snails, slugs, and land snails. They possess a soft body and a muscular foot, which they use for locomotion. Mollusks have successfully colonized various terrestrial environments.
10. Echinoderms

Although echinoderms are primarily associated with marine ecosystems, some species can be found in intertidal zones or even on land. These unique creatures, like certain sea stars and sea urchins, have developed adaptations to withstand exposure to air and survive in challenging conditions.
11. Annelids
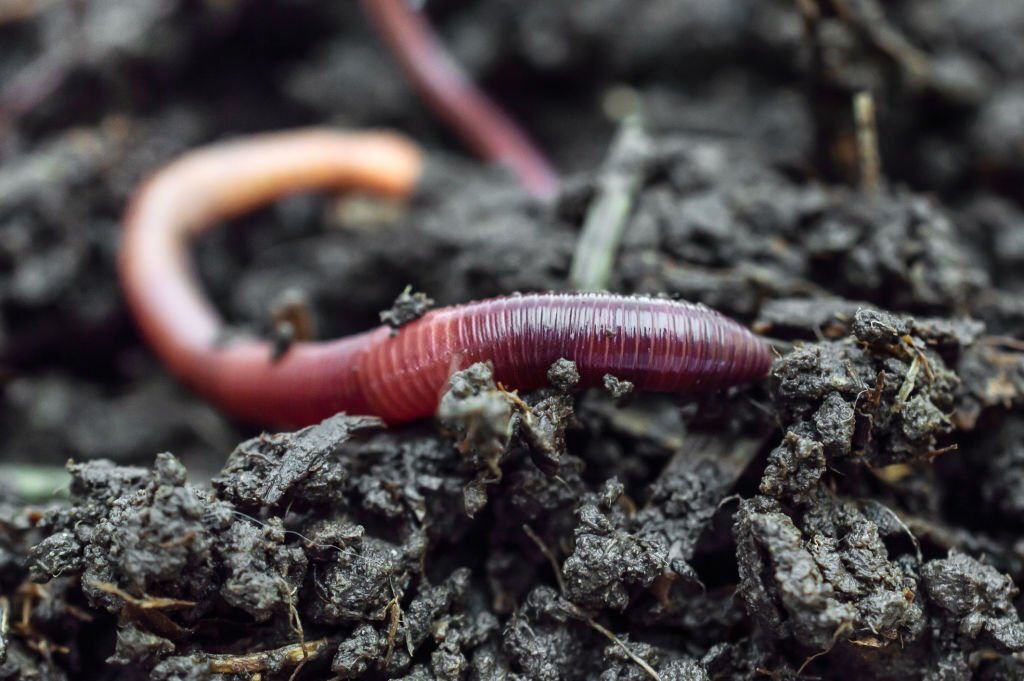

Annelids, which are segmented worms, also have representatives that inhabit terrestrial environments. Earthworms, for example, are essential for soil health and nutrient cycling. They play a vital role in improving soil structure and promoting plant growth.
12. Nematodes
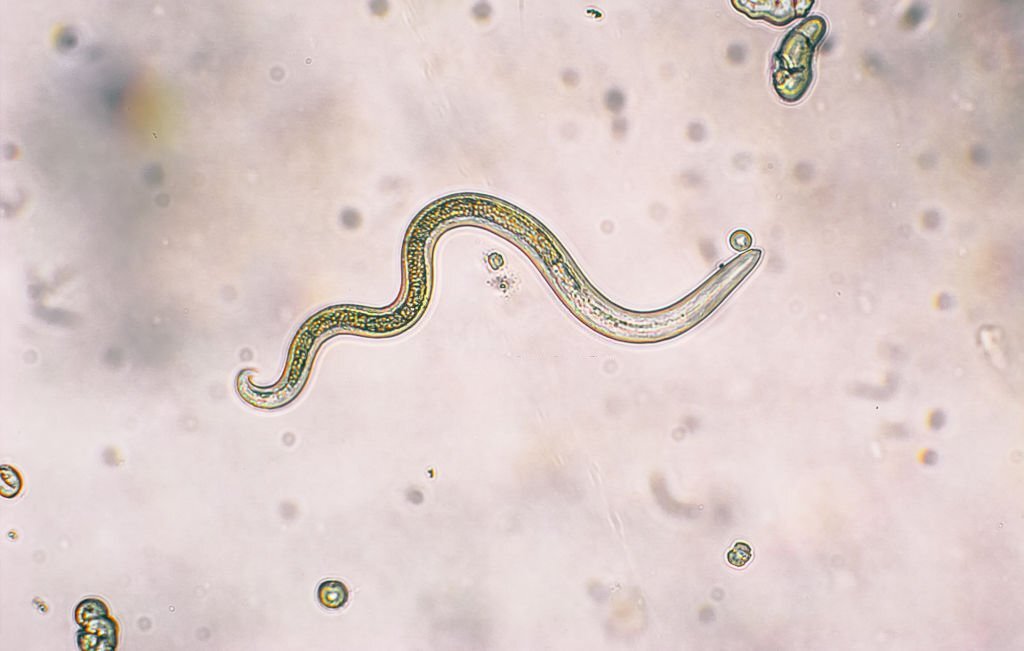
Nematodes, or roundworms, are incredibly diverse and ubiquitous in various habitats, including land. These microscopic creatures can be found in soil, decaying organic matter, and even as parasites in other animals. Nematodes play important ecological roles and have significant impacts on nutrient cycling. Also Read What kind of animal is a cobra Telenor?
13. Platyhelminthes
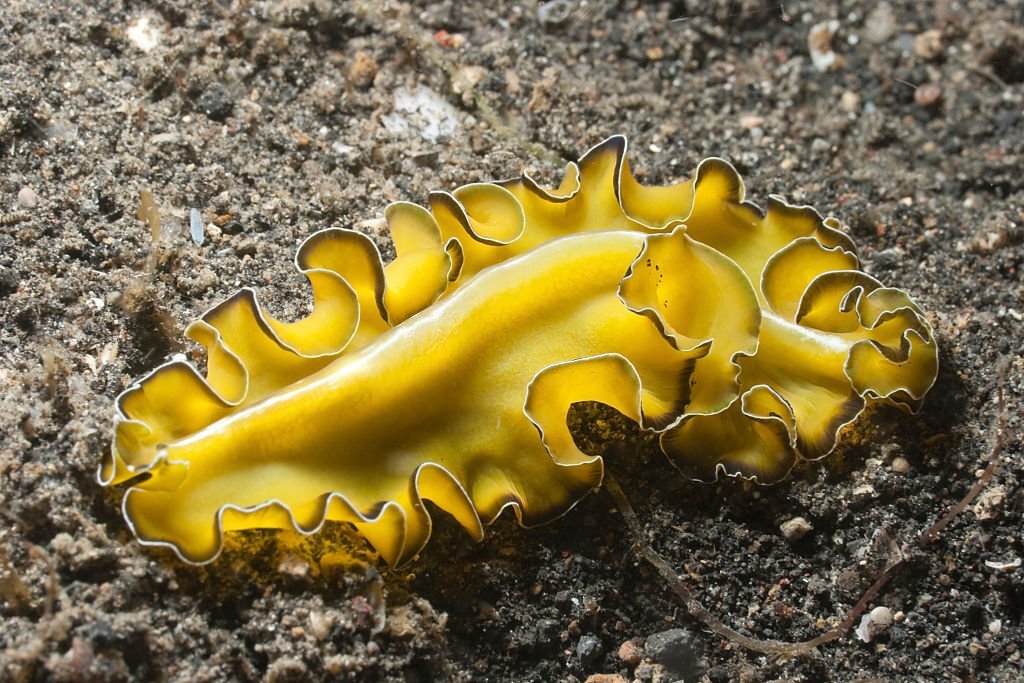

Platyhelminthes, or flatworms, are a group of land animals with flattened bodies. While many flatworm species inhabit aquatic environments, some have adapted to life on land. Land planarians, for instance, are free-living flatworms found in moist terrestrial habitats.
14. Cnidarians
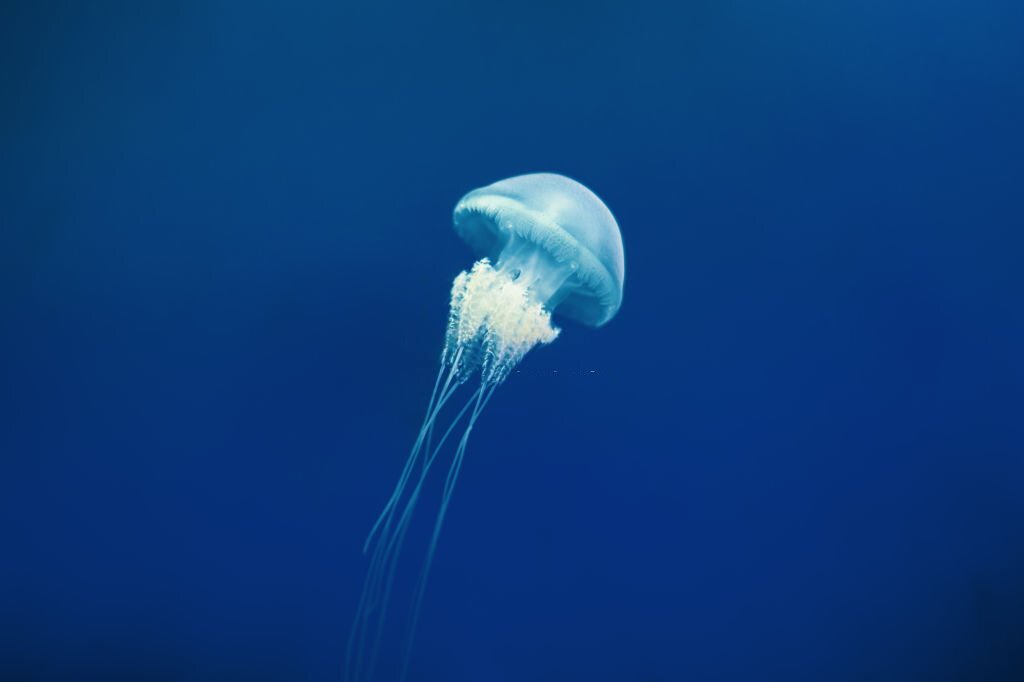

Cnidarians, such as jellyfish and sea anemones, are predominantly marine organisms. However, certain species, like the sea anemone, have adapted to live in intertidal zones or even on land. They display remarkable survival strategies to endure exposure to air and fluctuations in temperature.
15. Poriferans
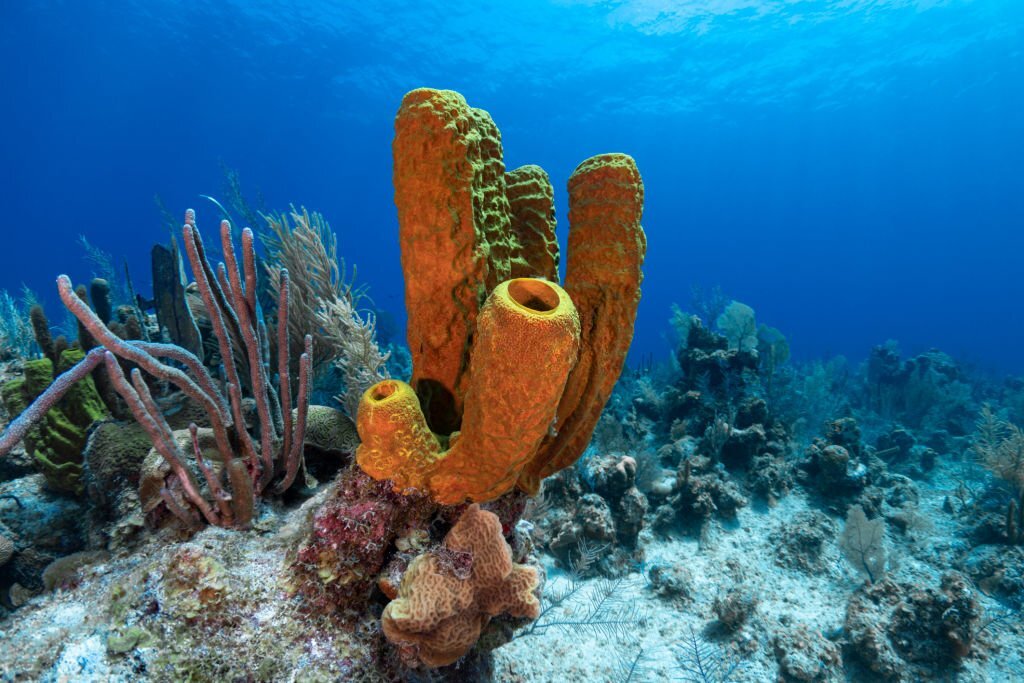

Poriferans, or sponges, are primarily associated with aquatic environments. However, some freshwater sponges have adapted to live in damp terrestrial habitats. These land-dwelling sponges rely on moist conditions to maintain their feeding and reproductive processes.
Conclusion
The world of land animals is incredibly diverse, comprising mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, and a plethora of other fascinating creatures. Each type of land animal has unique adaptations and characteristics that enable them to thrive in specific environments. Understanding and appreciating this diversity enriches our knowledge of the natural world and highlights the intricate web of life on land.
FAQs
What are some examples of carnivorous land animals?
- Examples of carnivorous land animals include lions, tigers, wolves, and cheetahs.
Which land animals are herbivores?
- Some herbivorous land animals include elephants, giraffes, deer, and rabbits.
Do all land animals lay eggs?
- No, not all land animals lay eggs. Some give birth to live young, such as mammals, while others lay eggs, like reptiles and birds.
How many legs do insects have?
- Insects typically have six legs.
Are crustaceans considered land animals?
- While crustaceans are primarily aquatic, certain species have adapted to terrestrial habitats, making them land animals as well.